Contents
Introduction
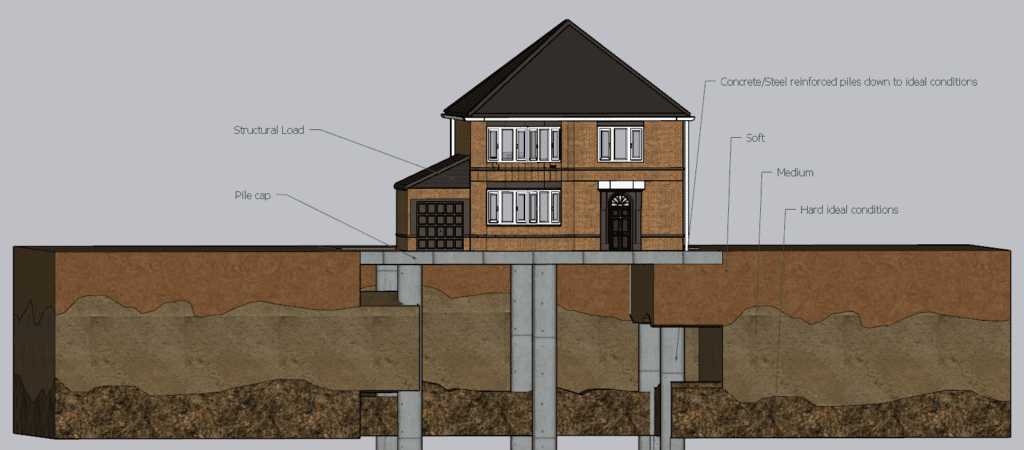
A pile foundation is a particular kind of deep foundation that is often used to support constructions that are subjected to significant loads. Piles are long, slender columns which are driven into the ground to a depth where they can bear the load of the structure. Pile foundations are used when the soil is not strong enough to support the weight of the structure and when the depth of the foundation is too great for a shallow foundation.
What is pile foundation?
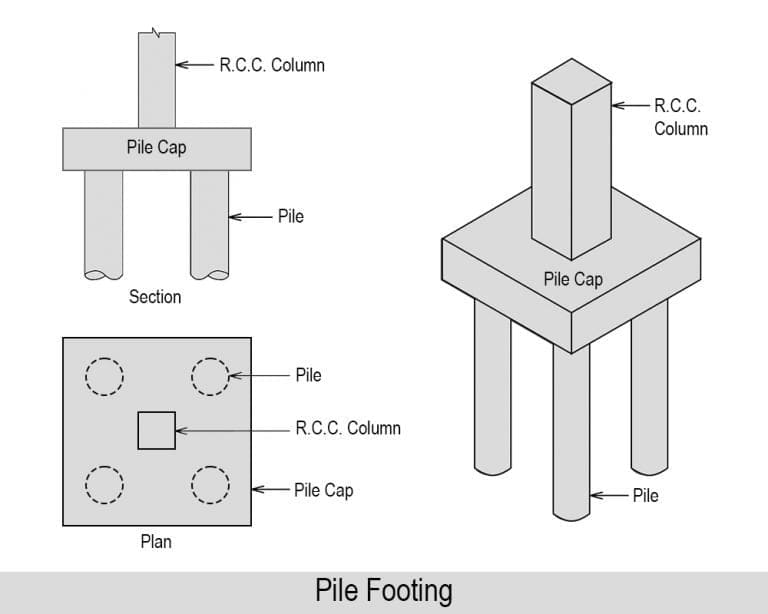
Pile foundations are deep foundations that are used to transfer loads from buildings and other structures to deeper, more stable layers of soil or rock. Piles are usually made of concrete, steel, or timber. They are driven into the ground, either manually or using special equipment, until they reach a depth where the load-bearing capacity of the soil or rock is sufficient to support the structure.
Pile foundations are often used in areas where the ground is too weak to support the weight of the structure, or where the water table is too high. They are also used to support structures that are located on slopes or in areas prone to landslides.
When to Use a Pile Foundation
A pile foundation is a form of groundwork that is deployed in circumstances in which the soil is unable to sustain the weight of the building for which the foundation is being constructed. Pile foundations are used in order to transfer the weight of the structure to a layer of soil that is both deeper and more solid. There are certain construction sites where the use of a pile foundation is the one and only viable option.
Types of Piles Foundations
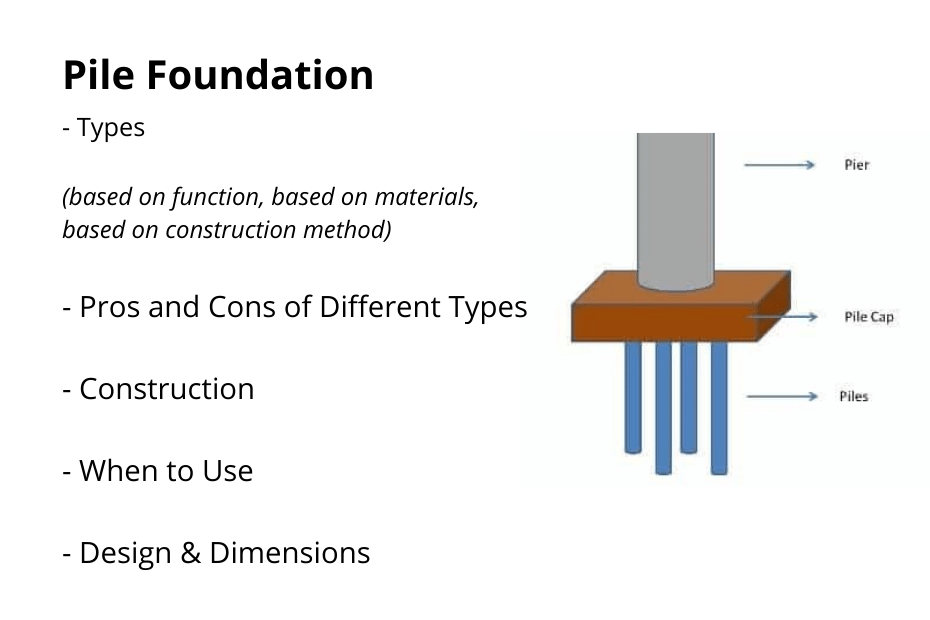
There is a diverse selection of pile types available for use in applications with different kinds of soil and distinct structural prerequisites. It is possible to categorise piles based on the primary purpose of their design (end-bearing, friction, or a mix of the two), as well as the building technique that was used like displacement or replacement bored.
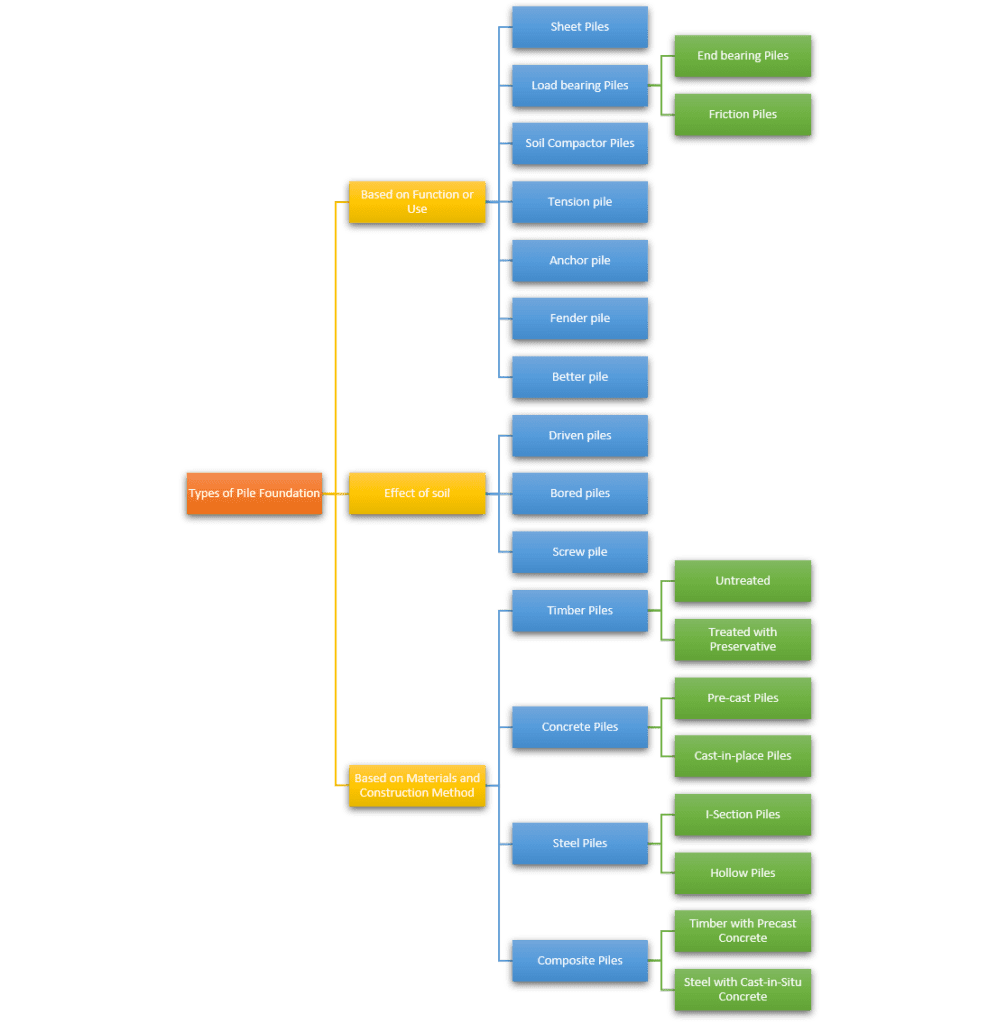
Types of pile foundations based on function or use:
With the introduction of reinforced concrete, there has been a development in the construction of foundation structures, which can be of great significance in terms of strength and endurance. The stress levels of reinforced concrete foundations have been greatly increased by the incorporation of steel reinforcement and the reinforcement bars were also oriented in a vertical plane.
Sheet piles
The sheet pile serves the following functions in the construction process.
- to create a separation between the foundation soil and the lateral soil.
- to restrict the flow of groundwater, which is an essential step in the construction of the cofferdam.
- in order to stop the vibrations from the machine from going through to the side structure.
- In order to construct a maintenance wall for maritime installations such as docks and wharves.
- In order to stop the erosion of the riverbanks.
- to provide assistance in maintaining the sidewalls of the foundation trench.
- to construct an embankment wall below the dam.
- Increasing the soil’s ability to hold soil and keep confined.
to stop the foundation of the river from being eroded away by the water of the river or the sea.
Load Bearing Piles
The form of pile foundation known as a load bearing pile, as opposed to a sheet pile, is the kind of pile that transmits the vertical loads of the structure to the soil below it. These foundations move loads across sections of soil that have inadequate supporting properties and onto layers of soil that are better suited to sustain the load. Load-bearing piles may be again classified into two different categories depending on the the mechanism by which loads are transferred from the pile to the ground.
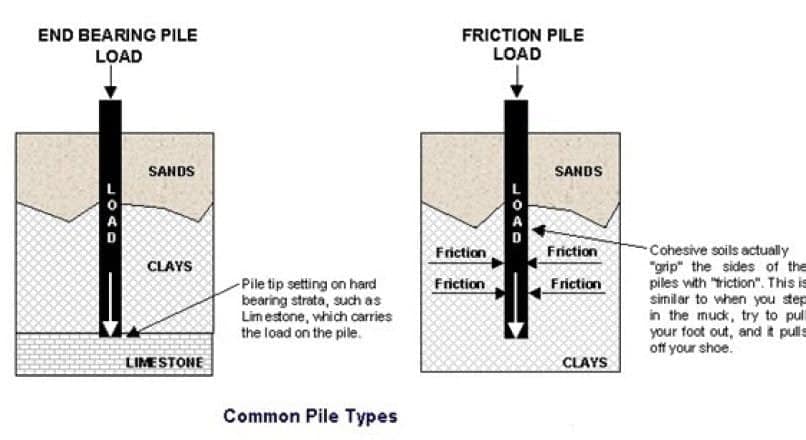
End Bearing Piles
When using a pile constructed in this manner, the loads go via the lowermost point of the pile. At the lowest part of the pile, there is a strong layer of earth or rock that serves as a support for the base of the pile. In most cases, the pile will be found resting in a transition layer between a weak and strong layer. As a direct consequence of this, the pile performs the function of a column and distributes the load in a reliable manner to the sturdy layer.
Multiplying the area of the pile’s tip by the bearing capacity of the soil at the precise depth at which the pile sits in the earth is one way to calculate the overall capacity of an end-bearing pile. This may be done to estimate the overall capacity of an end-bearing pile. Calculations are done to determine the diameter of the pile while taking into consideration an appropriate factor of safety.
Friction Piles
One kind of pile foundation is called as a friction pile. To transmit the weight of the superstructure, this sort of pile makes use of the frictional resistance force that exists between the pile surface and the earth that is near to it. It is necessary for the friction force to be sufficient to sustain the superstructure in order to have a foundation that is stable.
Proper evaluation of the skin friction that is expected to occur at a pile surface, together with the consideration of an appropriate factor of safety, should be carried out.
How Can the Capacity of a Friction Pile Be Increased?
It is possible to improve the friction pile capacity by increasing the pile diameter, depth, number of piles, and roughness of the pile surface, among other things.
Soil Compactor Piles
This approach involves inserting a pipe into the ground, producing lateral movement and compaction of the soil around it, and then gradually removing the pipe and filling it with sand. This is how the sandpile is formed.
Also read: Isolated footing advantages and disadvantages- Types, Benefits & How to use
Pile foundation type based on the effect of soil
Driven piles
The construction of driven piles requires stringent adherence to tolerance standards, the use of high-strength materials, and careful attention to quality control. Conformity to BS 8004:2015 as well as standards established by the EC and inspections performed prior to installation to verify the product’s integrity help ensure quality that is consistent.
It is essential that driven piles keep their shape during the installation process and that successive piles do not cause them to become deformed in any way.
Bored piles
Bore piles are cylindrical structures composed of concrete (with or without reinforcing), and they may be erected in the ground using a number of different installation techniques.
Screw pile/ Helix pile foundation
As a direct consequence of the helical foundation system’s adaptability as well as its cost-effectiveness, the usage of helical piling and piling piers has become more commonplace. Because it is possible to use helical pile foundations in both compression and tension applications, the constructed foundation system is an appealing solution for the building of deep foundations.
Also read: Combined Footing Design, Types, Dimensions, Adv. & Disadvantages
Due to the ease with which they may be installed, helical piles are available at an economical cost. They are available in a variety of lengths and thicknesses, as well as being precisely constructed to accommodate the needs of the application and the ground conditions. The helical pile is a flexible, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective technique that has various applications throughout the civil engineering industry, including but not limited to the construction, and transportation sectors.
Based on the materials, there are different types of pile foundations.
Timber piles
Timber remain for roughly 30 years on average. They come in a variety of shapes, including rectangular and round. They may range in size from twelve to sixteen inches in diameter. The pile is typically twenty times the width of the top.
They are normally built to hold 15 to 20 tonnes of weight. Bolting fish plates to the sides of the piles might provide additional strength.
The Benefits of Timber Piles-
- There are regular-sized timber piles available.
- Economical.
- It’s simple to set up.
- There’s a small chance of damage.
- After they’ve been placed, timber piles may be trimmed to any length.
- Timber piles can be simply removed if required.
Timber Piles Have a Few Drawbacks-
- Longer-length piles aren’t generally available.
- Straight piles are difficult to obtain when the length is short.
- If the soil layers are particularly hard, driving the pile is tough.
- The use of timber or wooden piles as end-bearing piles is not recommended.
- Special precautions must be taken to ensure the long-term endurance of wood piles. Wooden piles, for example, are often coated with preservatives.
Concrete Piles
Pre-cast Concrete Pile
The Benefits of Pre-cast Piles
The pile’s quality may be managed.
If a problem is discovered, it may be repaired before driving.
Underwater driving of pre-cast piles is possible.
After the piles have been driven to the requisite length, they may be loaded immediately.
Pre-cast Piles Have Some Drawbacks
It is difficult to extend or reduce the length of the pile once it has been chosen.
It is tough to mobilise them.
To drive, it needs a lot of pricey and heavy equipment.
During the handling and driving of piles, there is a risk of breakage or damage.
Steel piles
Steel Piles Have a Lot of Benefits
They are simple to set up.
When compared to other types of piles, they may reach a larger depth.
Because of the smaller cross-sectional area, it may penetrate through the hard layer of soil.
Splicing steel piles is simple.
Can carry a lot of weight.
Steel piles have few Drawbacks
Corrosive in nature.
Has the potential to deviate when driving.
Expensive in comparison.
Pile foundation Details
Fundamental actions that need to be taken in order to construct the pile. In connection to the cast in situ piles, the following technique will be explained.
The following variations, known as permitted tolerances, are recognised by various standards as being acceptable throughout the building process.

Steps of Pile Construction and Important Aspects to Consider
Putting into action the preliminary preparations
To get started, remove the topsoil up to the level of the rock. Despite the fact that there is a typically acceptable tolerance of 75 millimetres, it must always make an effort to keep the pile in the same location as it was shown in the designs.
Beginning rock coring while monitoring the depth at which you are beginning rock coring. When this occurs, it is imperative that the coring be performed on a fresh hard surface and not on a rock that has been exposed to the environment.
It is to be measured using samples, rates of penetration, data from drill logs, and any other site-specific pile depths that may exist.
Because it is so difficult to find new rock, closer to a borehole, the first plie will be made than it was originally planned. After that, one may proceed to assess the remaining parameters. On the basis of it, we are able to go on with the piling.
In order to evaluate the rock’s quality, visual observations are performed.
In addition, techniques of testing like as the point load test might be used in order to determine the rock’s tensile strength. The results of the point load test may be combined in order to determine the end bearing of the pile. In the event that it does not meet expectations, rock coring will continue until the sound rock is located.
After the coring has been finished in the rock to the specifications of the socketing lengths, cleaning will take place.
The removal of mud, sand, and other impurities from the bentonite should be the primary focus of the cleaning process. This process is also known as flushing.
There are factors that need to be looked for in order to assure that the pile is clean enough. The limiting values are shown in the figure that follows. The values for those parameters will shift from one specification to the next.
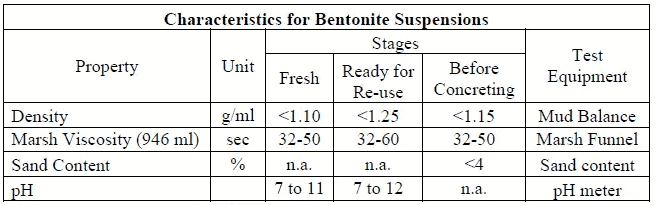
The flushing is stopped as soon as the amount of bentonite in the excavation approaches the limitations that were defined.
The tremie pipe is then positioned into the excavation after this step.
After that, the tremie receives a gradual addition of concrete. After the tremie has been filled, it is elevated by a very little amount, which allows the concrete to flow out of the opening.
This concrete, along with all of the dirt and other pollutants that are at the bottom of the pile, will eventually rise upward. The tremie is once again loaded with concrete and then opened up to let more concrete flow out.
It will assure that the tremie pipe’s end is consistently positioned inside the freshly mixed concrete. It makes it possible for constantly new concrete to mix with fresh concrete, and it also allows the top concrete layer to gradually move upward.
In addition, the pace at which the concrete is poured has to be managed carefully in order to prevent the reinforcing cage from being lifted. The cage will be opened up in the event that the rate is greater.
It is necessary to continue doing this until the concreting is finished.
Pile foundation design
After the piles have been chosen as the form of foundation to be used in accordance with the instructions provided in the geotechnical study report, an assessment of the required number of piles must be carried out. The capacity of the pile is then required.
When determining the pile capacity, there are two components that are used in the pile foundations
- Geotechnical Design
- Structural Planning and Design

Piles Geotechnical Design
The soil condition and the rock condition where the pile will be moored are taken into consideration while conducting the geotechnical capacity evaluation of the pile.
The following equation may be used to provide a representation of the geotechnical capacity of the pile:
Qp + Qs= Qu
The permissible capacity, denoted by Qall, may be determined by using the formula:
Qall = Qu / FoS
The factor of safety, often known as FoS, ranges from 2.5 to 4.
In addition, the maximum load that can be supported by the pile may be determined in a number of different ways. The manner in which the factor of safety is used could be different from one nation to the next depending on the norms that are in place there.
It has noted that a low FoS, such as 2.0, is also used for skin friction. It is strongly advised that while designing it to adhere to the local norms.
Structural Design of Pile foundation
In majority of the standards, in bored cast in situ piles, 0.25fcu is considered to be the maximum permissible concrete stress. There is just a very little amount of variation.
The pile, on the other hand, has to be checked for buckling, particularly when it is erected on a weak ground. As a consequence of this, buckling analysis is performed on piling foundations.
And taking into account the same, structural design as well as the design of the reinforcement may be done.
When it comes to the design of a pile, there are two different approaches/steps.
Determine the Critical Buckling Load, and then check to see whether it is higher than the load that is now being applied to the structure.
Execute out more thorough buckling analyses, as well as the design, and then carry them out.
The following is a synopsis of the stages involved in the calculation:
Step 1
Determine the critical load that causes buckling (Pcr).
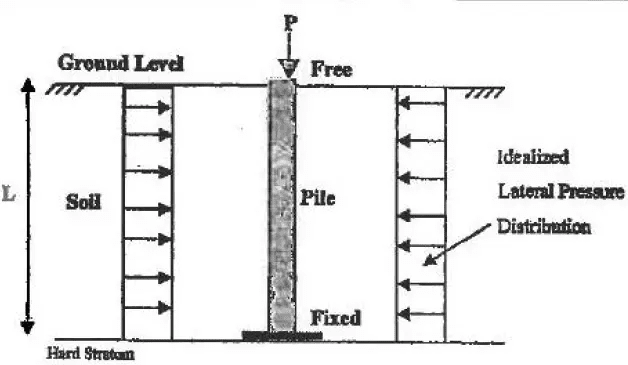
Step 2
When calculating the effective length of the pile, it is important to take into consideration the PCR, soil springs, and rotation at the top of the pile (which may have some rotational fixity) (Lcr).
Step 3
Since we are known of the weights that will be applied, the effective length, and the pile diameter, we are able to design the pile using either the traditional approach or a software application. The following is a summary of the most important aspects that should be addressed while designing the piling foundations:
- Evaluate the pile’s geotechnical capacity as well as its structural capacity, and use whichever of the two capacities is lower as the pile capacity.
- Divide the capacity of the pile by the load that is being applied (either the column load or the applied load); this will tell you the serviceability limit state for the number of piles needed.
- When there is more than one pile that has to be designed, the individual loads for each pile need to be determined by calculating the distance between the load centre and the geometric centre of each pile. It is necessary to allocate loads in accordance with the location of the pile.
- If 2 or more pile is present, the shortest distance between them must be 2.5 times the diameter of the pile.
- Because the distance between the piles will now be greater, using the truss analogy to the design of the pile cap will no longer be possible. As a result, the distance between piles is kept at 2.5–3 times the diameter of each pile.
- When organic soils are present, careful consideration has to be given to the potential for adverse skin frictions. Otherwise, the capacity of the pile cannot be accurately estimated.
- In the case of weak soils, for a greater depth, pile bucking has to be monitored and controlled.
- When determining the socketing lengths, careful consideration must be given to the RQD and CR values.
- The majority of standards agree that a tolerance of 75 millimetres should be allowed for construction deviations. This will be taken into consideration when designing the pile cap. When there is just one pile, particular care and attention must be taken. The ground beams are going to be responsible for carrying the moment that’s caused by the centricity. As a result, it has to be taken into account while designing the ground beam.
Conclusion
Pile foundations are most commonly used in situations where the ground is too weak to support the weight of the structure. There are a lot of potential causes for this, including a high water table, poor soil conditions, or seismic activity.Pile foundations are also used when the structure is too tall to be supported by a traditional foundation.

It sure was interesting when you said that in circumstances in which the soil is unable to sustain the weight of the building, a pile foundation becomes beneficial. This reminds me of my aunt is planning to have a 7-story building constructed for her next year. Maybe, she can consider the benefits of piling foundations, especially when ensuring the stability and safety of her building.
I appreciate your explanation when you informed us that a pile foundation is deployed as a form of groundwork used to transfer the weight of the structure to a layer of deeper and more solid soil where the foundation is being constructed. I will be investing in a 5-story apartment complex in Victoria next year, so I need to make sure the construction of the building is sturdy and stable to keep the tenants safe. I’ll take note of this while I look for a piling contractor in Victoria to hire for this building project soon.
You got my attention when you said that helical piles are flexible, so they can easily be installed at an economical cost. This makes me think of finding a highly recommended manufacturer of helical piles before the construction of my four-story property starts in February next year. I want to ensure that the manufacturer that I will find can offer me the best possible deal so I can save money and make a cost-effective choice at the same time.