Raft foundations
These are used in locations where other kinds of shallow foundations do not fit in an appropriate manner. When the structural load is quite significant, these are the kind of foundations that are employed. It is constructed as a single mat that is comprised of all of the load-bearing parts of the structure. Its purpose is to avoid differential settling of single footings.
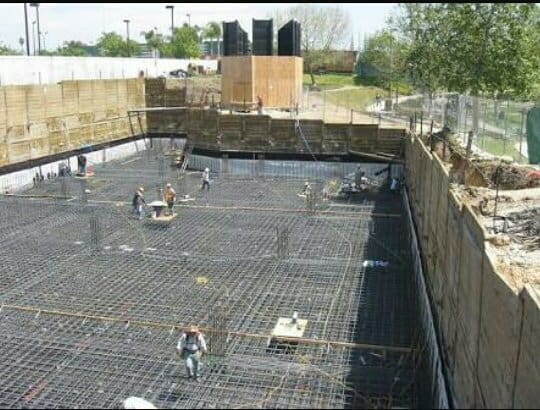

The usage of a raft foundation includes:
- For weaker soils and a vast region over which the weight is to be distributed.
- It is not possible to use any other kind of shallow foundations.
- It is necessary to avoid differential settlement.
- It is possible to use mat footing in situations when a shallow foundation is required, but the soil quality is unsatisfactory.
Raft foundation’s Drawbacks and Limitations
- The base of the raft is vulnerable to edge erosion.
- In certain instances, the raft foundation needs a greater quantity of reinforcement, which will eventually result in an increased cost.
- When contrasted to other foundations, this one requires skilled labourers to be employed.
- When a concentrated load is exerted on the mat or raft (also known as a point load), special care and attention is required.
- The base of the raft needs more steel and concrete, which means that the cost will be higher.
Read more: Combined Footing Design, Types, Dimensions, Adv. & Disadvantages
Raft foundation Design
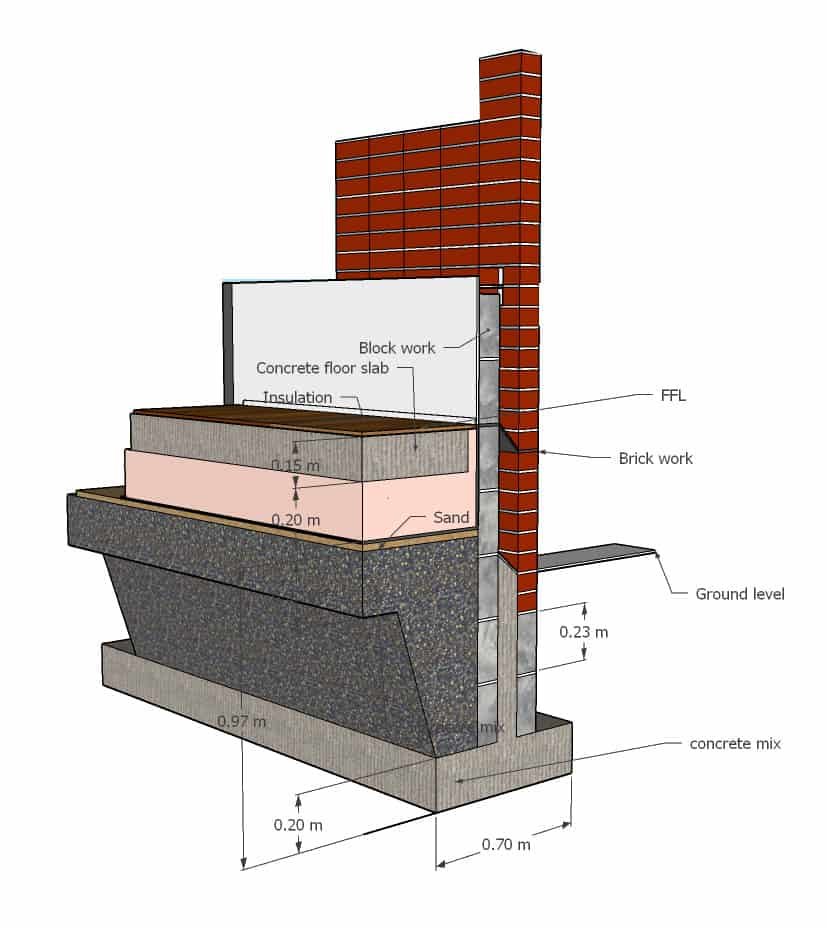
Excavation
Before constructing a raft foundation, the land must first be excavated to a level that is both consistent and flat.
The location of the foundation will need to be inspected and dug to a depth that is equal to or greater than the depth to which the foundation will be erected. In order to prevent uneven settling, the base of the excavation has been levelled.
If, after excavation, the soil is found to be moist or if the water table has been reached, pumping will be performed to remove the water and additional excavation will be begun.
Read more: Isolated footing advantages and disadvantages- 3 Types, Benefits, How to use
Waterproof membrane
To prevent water from penetrating the slab, a waterproofing membrane has been installed at the foundation. After waterproof plastic sheet is laid over the ground, then a three-inch-thick layer of plain cement concrete (PCC) is poured on top of it. This is done to provide a basis for the foundation that is absolutely smooth and level.
Waterproof Coating
After this step is complete, a coating of waterproofing is applied, and then the reinforcing steel for the raft slab is secured into place.
Once the concrete has been poured, a cement-sand paste is applied in order to ensure that the concrete will bond with the soil. The concrete is poured to the appropriate thickness. For small structures, it is typically between 200 millimetres (8 inches) and 300 millimetres (12 inches) thick; however, this may be much thicker if intended to carry large loads.
Laying of Reinforcement
After this step will need to lay the reinforcement, which must be finished before the foundation is concreted so that the concrete work may be done in one continuous motion.
Pouring of Concrete
Following the completion of the slab’s depth measurement, the concrete is next poured in accordance with the specified height, and it is allowed to cure in a number of different methods.
Types of Raft Foundations
Flat Plate Mat
This is the most basic configuration for a raft’s understructure. When the columns and walls are consistently placed at short intervals and the weights that are given to the mat are relatively minimal, this particular sort of mat is used.
Reinforcement is added in both directions, and further reinforcement is needed at the positions of the load-bearing columns and walls. Due to economic considerations, the thickness of this kind of raft foundation is often limited to no more than 300 millimetres. A slab that is much thicker would not be cost-effective.
As a result of the provision of reinforcement in both directions, the foundation may give resistance to moments in both the respective directions.
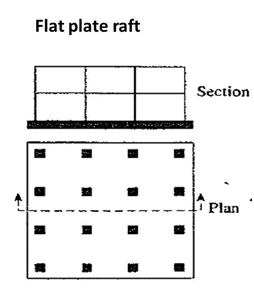
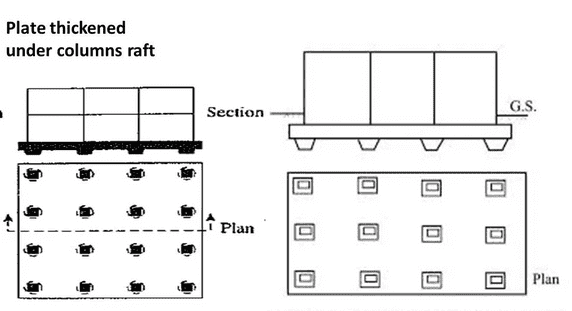
Plate Thickened under Columns
When the load-bearing columns and walls are subjected to greater loads, the slab underneath them is expanded, and more reinforcement is added to prevent diagonal shear and negative reinforcement. This is done so that the structure can withstand heavier loads.
To achieve this goal, more reinforcement is added to the thicker slab so that it can withstand the additional load and, in turn, transmit the weight to the soil in the appropriate proportion.
Because of this, the diagonal shear that is applied may be accommodated by this kind, which means that negative reinforcement is taken into consideration.
Two-way Beam and Slab
In this particular kind of raft, the beams and the raft slab that connects the columns and walls are both cast in one continuous process. When the columns are positioned at a greater distance apart and when the weights that are exerted on the columns vary, this form of raft is an appropriate choice.
When the excessive bending moment is to be resisted by column strips, it does not seem that there are any alternative sorts of Raft Foundation that would be helpful or inexpensive. In situations like these, a beam and slab raft is used, which seems to have a good chance of preventing undesirable bending movement.
To put it another way, when the load imposed by columns is both high and varied with the length of the footing, a foundation of the kind known as a Beam and Slab is created.
Beams of the appropriate dimensions are attached to each and every row of the column, both in the direction of the longitudinal axis and the direction of the transverse axis.
The remaining space, which will become the centre panels, will have slabs installed there that will be supported by grid beams or walls.
The Beam and Slab type raft foundation serve the same purpose as the thickening flat slab raft foundation, but it offers more protection against excessive bending movement brought on by unequal loads.
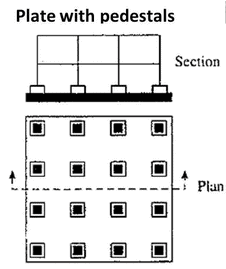
Plates with Pedestals
At the bottom of the columns that make up this kind of mat is a pedestal that supports them. This form of foundation serves the same function as a flat plate that has been thickened beneath columns.
Piled Raft
The raft foundations that take the form of piling support are one kind. When the soil at a shallow depth is extremely compressible and the water table is high, a piled raft is used. The use of piles beneath the raft both helps to prevent it from sinking and offers resistance to its buoyancy.
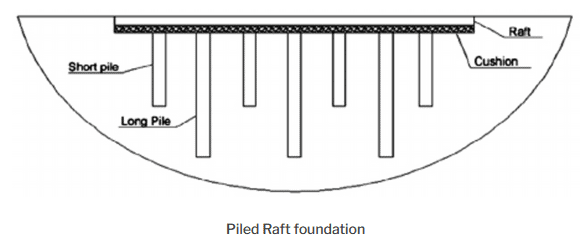
It is possible to create what is known as a piled raft foundation by supplementing a normal raft foundation with piles in situations in which the conventional foundation does not provide sufficient support.
Structures get support from their foundations, which transmit the loads that the structures exert onto layers of soil or rock that have enough load-bearing capability and features that are acceptable for disposal.
Read more: Pile Foundations: Types of pile foundation, Design and Details
Cellular Raft Foundation and Rigid Mat Substructure
The foundation walls of this particular kind of raft serve the function of a deep beam. When columns are required to handle exceptionally large loads and the depth of the connecting beams is more than 90 centimetres, a rigid frame mat is used. A cellular raft foundation is created by placing two concrete slabs, one on top of the other, and then connecting those slabs to foundation walls in both directions. This creates the foundation. When the needed slab thickness is quite high, it is cheap to use this form of raft since it is highly robust.
In situations where there is a risk of the earth rising owing to the swelling of clay soils that expand when they get wet, which might influence the stability of the building and lead to damage, a foundation made of cellular rafts is often used.
Because of their highly stiff nature, cellular raft foundations are well suited for use on ground that is expected to sink in an uneven way.
Such foundations are more likely to be located in regions that have been heavily mined or fields with poor soil, both of which have significant bending moments that need to be resisted as a result of uneven settlement and upheaval.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mat is one of the most frequent and popular types of foundation system owing to the ease with which it can be constructed and its efficacy in areas with poor soil condition at a shallow depth. To make the most efficient use of the foundation, one must study the state of the soil and examine the loading conditions of the structure. Additionally, one must take the appropriate safety measures in order to ensure a safe construction.

Wow, this is a great post! Raft and mat foundations are such crucial elements in construction, providing stability and distributing loads effectively. I particularly found the insights on the differences between the two types enlightening. It’s impressive to see how technology and innovative design have impacted foundation engineering. Thanks for sharing this valuable information! #construction #engineering #foundations