The terms “centering” and “shuttering” are often referred to as “formwork.” The temporary structure that is used to support both vertical and horizontal surfaces during construction is referred to as “formwork.” This definition is simple enough to understand. It acts as a support structure while the concrete is drying.
Fresh concrete is given form by it, and wet concrete is given control by it. It puts the concrete in the position.
What is Centering
Formwork may also be referred to as centering. During the building process, this is done to ensure that the formwork for horizontal surfaces, such as floor beams and slabs, stays in place. It is required to function for a brief amount of time only. There are several approaches of centering.
The following are some of the many benefits of centering in construction:
- provides a base for the structure that is being formed
- provides the overall support
- Reduces the likelihood that any one component of the structure may become stressed.
- assures that the components are in the proper setting.
- ensuring the building does not collapse
- forms horizontal surfaces
- Support beams, slab bottoms, arches, vaults, shell-shaped buildings, and the like all need to have centering done.
There are several types of centering depending on the material used, including the following:
- Aluminium
- glass-reinforced material
- wood
- steel
Shuttering in Construction
Shuttering is a vertical Formwork. Its advantage is that the sides of the slabs are supported by the wall and the slabs are ready for cementing. Shuttering is also suitable for stairs and other vertical planes.
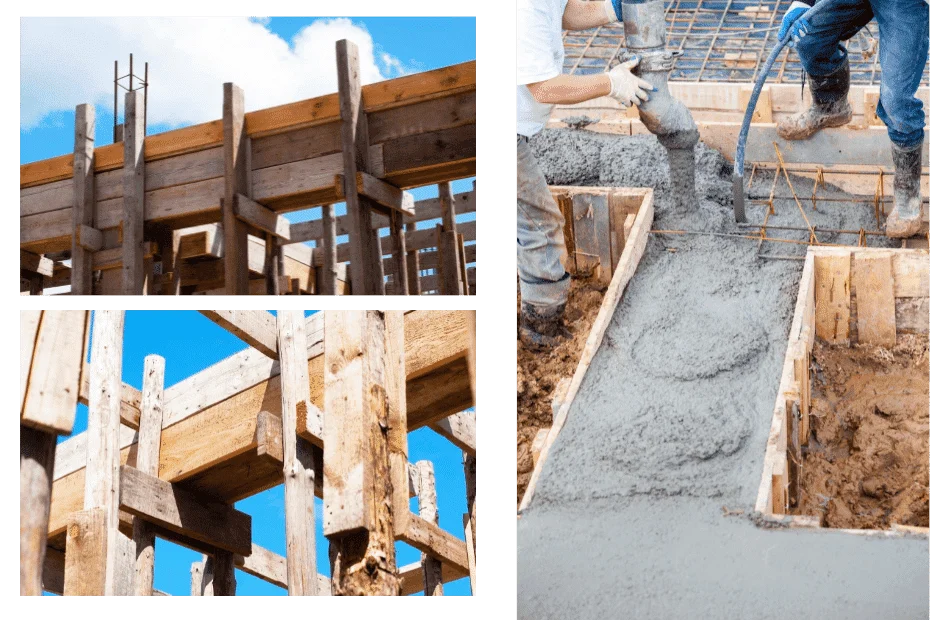

On the building site, shuttering is used to create a temporary mould into which concrete is poured in order to get the structural form that is needed. Wood is the material of choice for the construction of traditional shuttering; however, it is also possible to make shuttering out of steel, glass fibre reinforced polymers, and other materials.
Prerequisites for Shuttering
- It is important that the material be affordable in addition to being appropriate for several recyclings.
- It should be almost impervious to water, to the point that it does not pick up any moisture from the concrete.
- It should have sufficient strength to withstand any and all loads that are placed on it.
- It should have a sufficient degree of rigidity to ensure that deflection is kept to a minimal.
- It is important that the surface of the formwork be smooth, and that it allow for simple stripping.
Shuttering work
In the infrastructure and construction industries, shuttering work functions similarly to a mould in order to cast concrete components in a variety of shapes and sizes utilising a wide variety of materials, including but not limited to wood, steel, aluminium, and plastic. The word “form work” may sometimes be interchanged with the term “shuttering.”
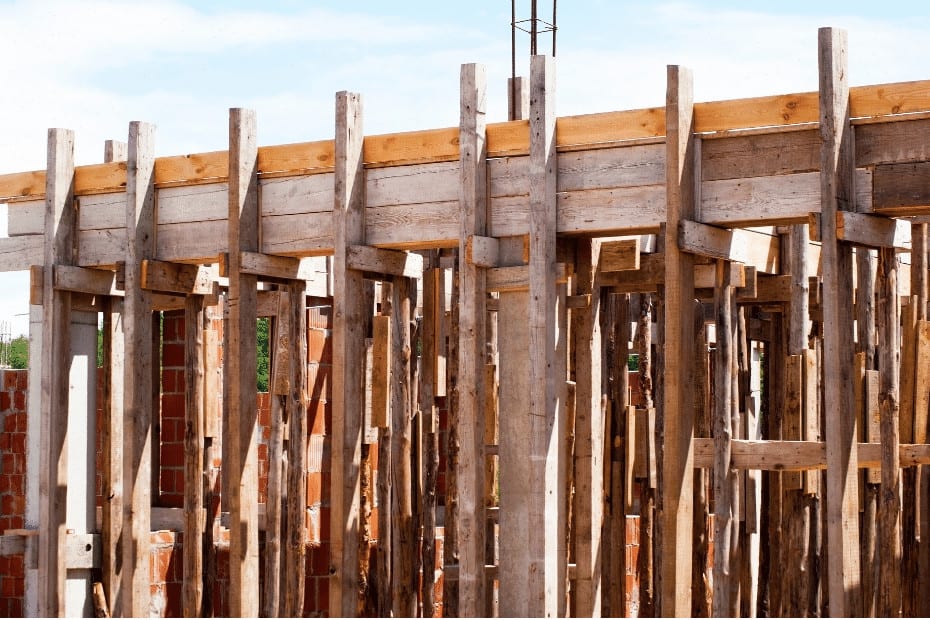

During the casting procedure of concrete and thereafter, until the concrete becomes firm and gains some percentage of the desired strength, it must have sufficient strength to sustain both the dead weight and the live load that is placed on it.
In the domain of structure, shuttering is a very important component. It has to have sufficient strength to support all of the loads that will be present while activities are being carried out, and then it needs to maintain its form while the concrete cures.
It is possible to utilise them as temporary or permanent moulds, which maintain the form of the concrete that has been poured into them until the concrete cures and becomes strong enough to sustain itself.
The shuttering acts as a mould for the construction of a building and the construction of its auxiliary components. Concrete is merely put in the mould in order for it to solidify and acquire sufficient strength at a later stage.
Work on the shuttering takes a significant amount of time to complete, and this spending accounts for 23 to 25 percent of the entire cost of the structure or building (and maybe much more). However, they are only temporary types of structures that are very necessary for supporting concrete while it gains the necessary amount of strength.
The Difference between Centering and Shuttering
Shuttering is a vertical Formwork, whereas Centering is a horizontal Formwork. Formworks for columns, walls, and sides of the beam, for example, are instances of shuttering, whereas the bottom of the slabs and the beam are examples of centering in a structure.
Shuttering and centering are important aspects of the structure. To provide a smooth working surface and homogeneous weight transmission, the slab floor should be exactly horizontal.
To eliminate eccentric loading, the column should be exactly vertical.
Shuttering Material
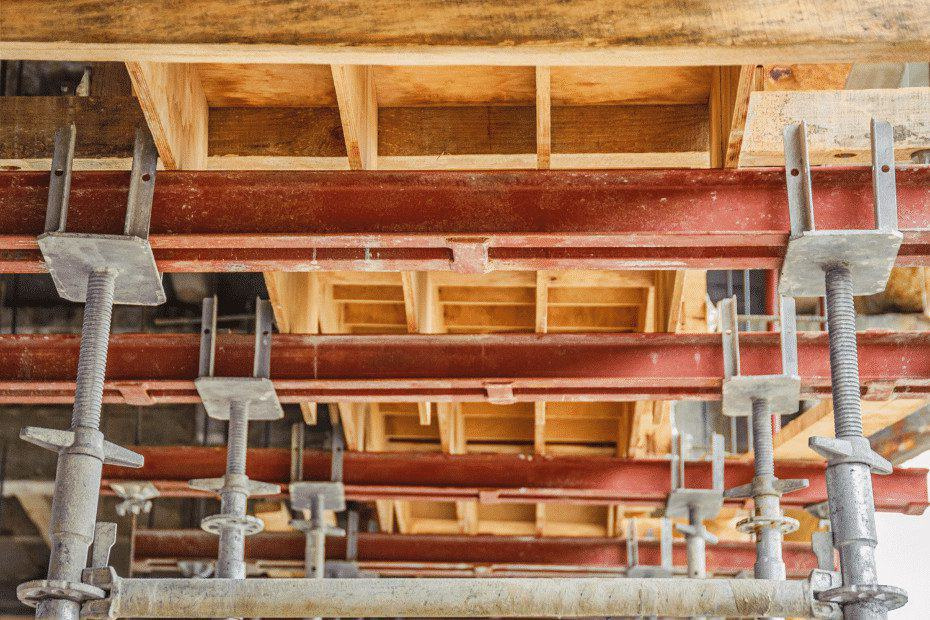

Despite the wide variety of formwork materials available, the following are some basic performance characteristics that are required to fulfil the requirements of concrete construction:
- ability to bear both dead and live loads combined.
- retaining its form by the use of appropriate supports and bracing.
- The joints ought to be watertight.
- Even though the formwork is easily removed, the operation itself must not harm the concrete in any way.
- Reusable material.
- The least heavy possible.
- The material used for the formwork must remain stable and not warp or deform.
Timber Shuttering
One of the first forms of formwork used in the building industry was made of timber. On-site assembly makes it the most versatile form, bringing with it a number of benefits, including the following:
- Simple to both build and remove.
- Lightweight, particularly when compared to formwork made of metal.
- workability, allowing for any form, size, or height
- Cost-effective for use in less extensive projects
- Permits the use of the area’s natural timber
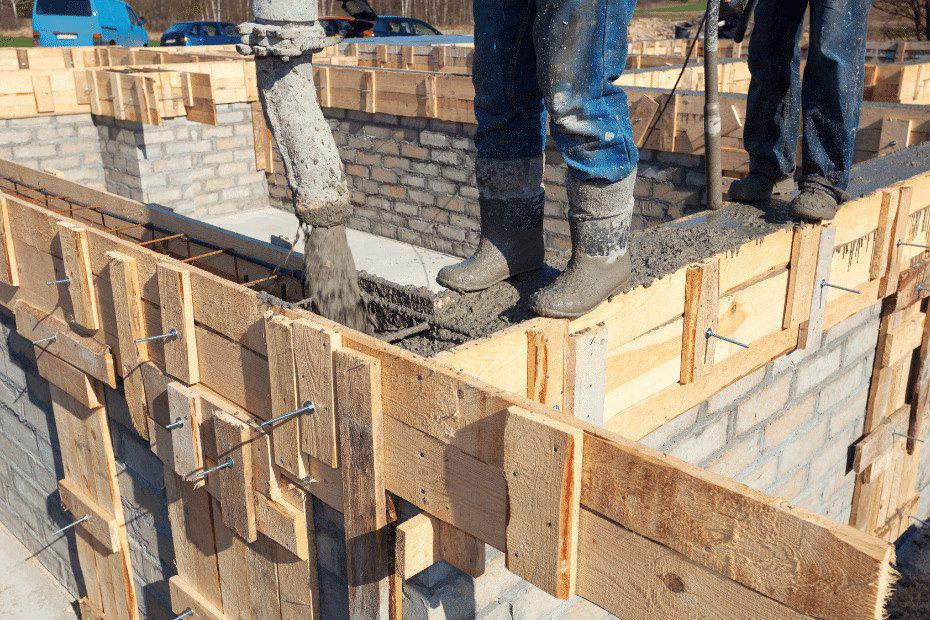

However, before selecting wood, its quality has to be thoroughly inspected, and need to make sure that it is termite-free. The use of timber formwork has two drawbacks that need to be taken into consideration: first, its limited lifespan, and second, the amount of time it takes to complete huge projects. When labour costs are minimal or when complicated concrete sections demand flexible formwork, the use of wood formwork is often advised as the appropriate option.
Plywood Shuttering
The traditional formwork method typically comprises standard plywood panels that are fastened together with wooden frames over their backs and walling, which are horizontal parts designed to withstand the weight and horizontal force of wet concrete.
Sheathing, decking, and form linings are the primary uses for plywood when it comes to applications involving formwork.
A formwork made of plywood has features that are comparable to those of a formwork made of timber, such as its strength, durability, and capacity to be lightweight.
Plywood boards may have a thickness of either 6 millimetres, 9 millimetres, or 12 millimetres. In general, the dimensions of a sheet of plywood are 8 feet by 4 feet.
When compared to the cost of shuttering made of timber, the cost of shuttering made of plywood is more affordable, given the following variables:
There is the possibility of having a smooth finish, which indicates that there is a surface finishing present.
When compared with shuttering made of timber, the number of reuses is much higher. For the sake of making an estimate, the number of reuses may be assumed to be between 20 and 25.
When it comes to the labour costs of mending and dismantling, some forms of shuttering provide for greater cost savings.
Advantages:
- Concrete has a smooth appearance as a result.
- a high proportion of strength to weight
- It is extremely easy to cut, and it may be shaped to meet any demand posed by the building phase.
- Plywood has the capacity to handle the irregular and temporary overloads that it may experience.
- Plywood maintains its structural integrity despite changes in both temperature and humidity.
Disadvantages:
- Cannot withstand heavy loads.
- Concrete water is absorbed by it, which causes the concrete’s strength to decrease.
- Plywood is more expensive than timber in most cases.
Steel or Metallic Shuttering
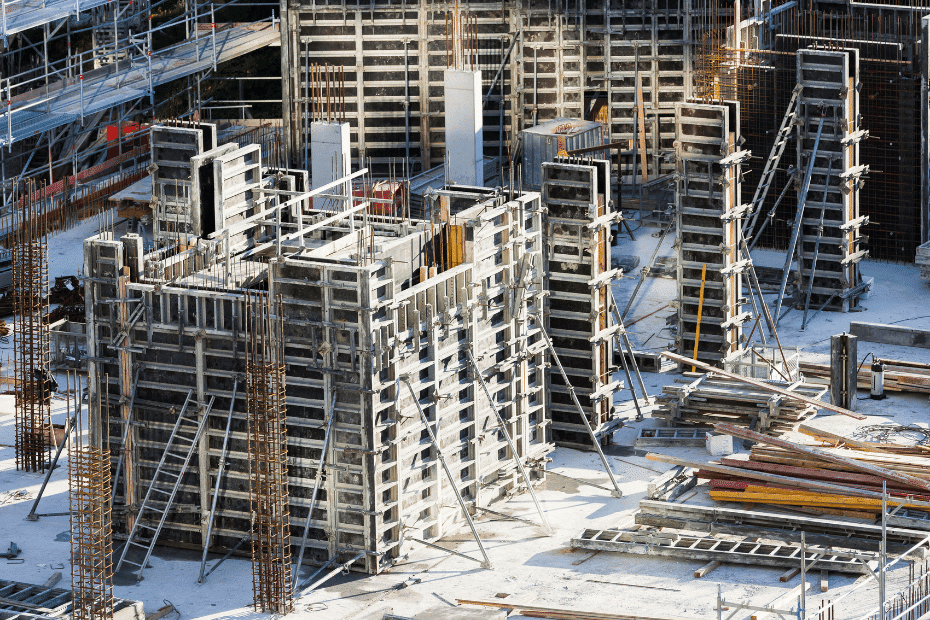
Panels for steel shuttering are typically manufactured out of very thin steel plates and are secured around the edges by very tiny steel angles. It is possible to use bolts and nuts or appropriate clamps in order to keep the panel components together. The building of bridges is the most common use for this kind of shuttering.
Steel shuttering is quickly gaining popularity as a result of the many times it may be reused during its lifespan. Although steel shuttering may be expensive, it is adaptable and may be utilised for a wide variety of projects and structures. The concrete surface may be finished with a highly smooth and flat appearance when steel shuttering is used. Tanks, columns, chimneys, sewers, tunnels, and retaining walls are some examples of constructions that are ideal candidates for their use because of their round or curved shapes.
When compared to wooden shutters, the benefits of using steel shutters are as follows:
- It gives the surface of the member a very smooth and even finish.
- Steel shuttering is cost-effective, has a long lifespan, and is very robust.
- It prevents the honeycombing effect from occurring and is waterproof.
- It has reusability of more than one hundred times.
- The moisture that is present on the concrete surface is not absorbed by the steel shuttering.
- It is simple to assemble and take apart as necessary.
Aluminum Shuttering
The Aluminum Formwork System in India is a relatively recent technology that helps save time and money while also improving the effectiveness of construction.
When it comes to above-the-plinth construction and the repetition of building schemes, aluminium formwork is a very cost-effective option.
It is one of the methods that has been regarded as being extremely ideal for the circumstances of mass building in India, where it is possible to attain a high degree of both quality and speed. The construction pace of this system has the potential to be faster than that of the vast majority of current building techniques and technologies. This procedure may be done effectively by the labour to speed up the construction process, provide quality control, and assure that the structure will last.
Advantages:
Because it is reused, it is efficient in terms of cost.
Because of its low weight, it is simple to operate, which results in increased productivity in the building.
Disadvantages:
Compared to the cost of Steel, Expensive
Because of the sudden overload, it might become bowed or deformed.
When aluminium formwork is employed, it is hard to make any adjustments to the structure.
Plastic Shuttering
Plastic shuttering may be constructed using interlocking panels or modular systems made of plastic, both of which are lightweight but very durable. Small projects with repeated operations, such as low-cost housing developments, benefit the most from it. It is suitable for use in the construction of basic concrete buildings.
The plastic shuttering is lightweight, and it can be washed with water. Additionally, it is appropriate for big areas and can be reused several times. The fact that many of its components are prefabricated is the primary reason for its poorer flexibility in comparison to wood.
This style of formwork is constructed out of interlocking panels or modular systems, both of which are composed of plastic that is both lightweight and durable.
The Many Benefits of Using Plastic Shutters
Plastic shuttering is one of the lightweight shuttering options available; as a result, it needs less money to be spent on handling and disassembly.
It is versatile enough to be employed for a significant portion.
Multiple reuses are feasible, provided they are transported and handled with care; the production process is very cost-effective.
Coffer Shuttering
Stay-in-place formwork is provided by the use of coffer shuttering. It is made up of two different filtering grids, each of which is strengthened by vertical and horizontal stiffeners and joined by articulated connections, all of which are foldable so that it may be transported on-site.
After the concrete is poured, the coffer shuttering is left in place as reinforcement. The coffer arrives at the construction site having been prefabricated at the manufacturer. These shutters are adaptable to any kind of construction, whether it an apartment building, high rise towers, etc
Fabric shuttering
Fabric Formwork, also known as Flexible Formwork, is an up-and-coming kind of shuttering technology that makes the building of complex and irregularly shaped structures easier.
Fabric formworks are sheets that are composed of synthetic fabrics and are porous.
The adherence of the cement mortar or paste that drains throughout the fabric is critical to the monolithic nature of the constructions that are formed out of these materials.
Advantages:
Reduces the amount of concrete required compared to more rigid formworks such as timber or steel.
Fabric formwork makes it feasible to build even the most complicated of architectural designs.
After the concrete has set, they are not difficult to remove.
Disadvantages:
Fabric formwork construction might, in certain instances, need more time to complete in order to make very complicated structures.
Conclusion
The part of the form work that supports the vertical surface is known as the shuttering. Some examples of shuttering are the sides of columns and beams, as well as the sides of slabs and walls.
The portion of the form work that supports the horizontal surface is referred to as the centering. Some examples of this are the bottom of the slab or the bottom of the beam.


